As time passes and collective morals change, the legacies of prominent figures in American history often evolve. The context in which these individuals earned their place in American memory becomes increasingly difficult to uncover.
Tag: Fort Donelson
-

The Battle of Shiloh
Two of the greatest Confederate generals in early 1862, Albert Sidney Johnston and P.G.T. Beauregard, rendezvoused in Corinth, Mississippi with a combined 42,000 men.[i] The city not only could serve as an origin point of a campaign into nearby Tennessee; it also was the meeting point for the Confederacy’s “main north-south and east-west railroads.”[ii] Given Corinth’s importance, Henry Halleck ordered Ulysses S. Grant to march his men to Pittsburg Landing, wait for his fellow general Don Carlos Buell to arrive with his army, and then move on Corinth as a combined force numbering approximately 75,000.[iii]
-
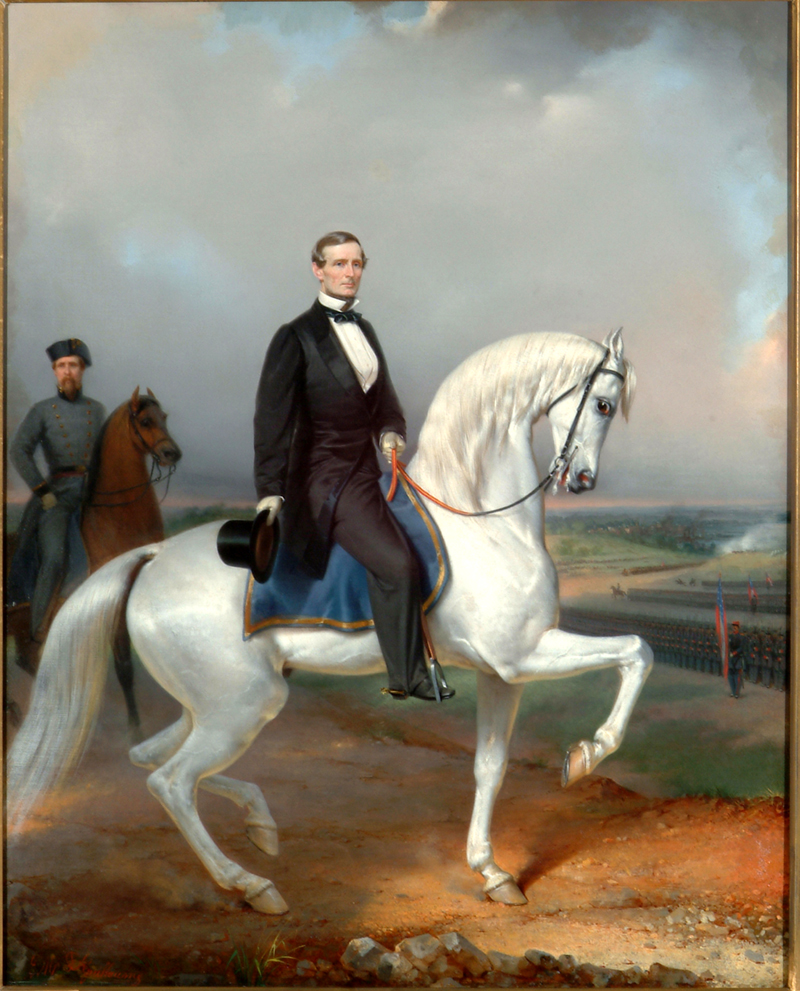

The Second Inauguration of Jefferson Davis
Confederate President Jefferson Davis, on the 130th anniversary of George Washington’s birthdate, was due to be inaugurated for a second time. Davis ran unopposed in the first (and only) presidential election in the Confederate States of America and was set to begin his six-year term on February 22, 1862. His daily responsibilities as president left him more involved in paperwork than any other activity, and the beginning of the day of his second inauguration was scarcely different from any other day for Davis: he did an hour of paperwork before preparing for the ceremony.[i] (more…)
-
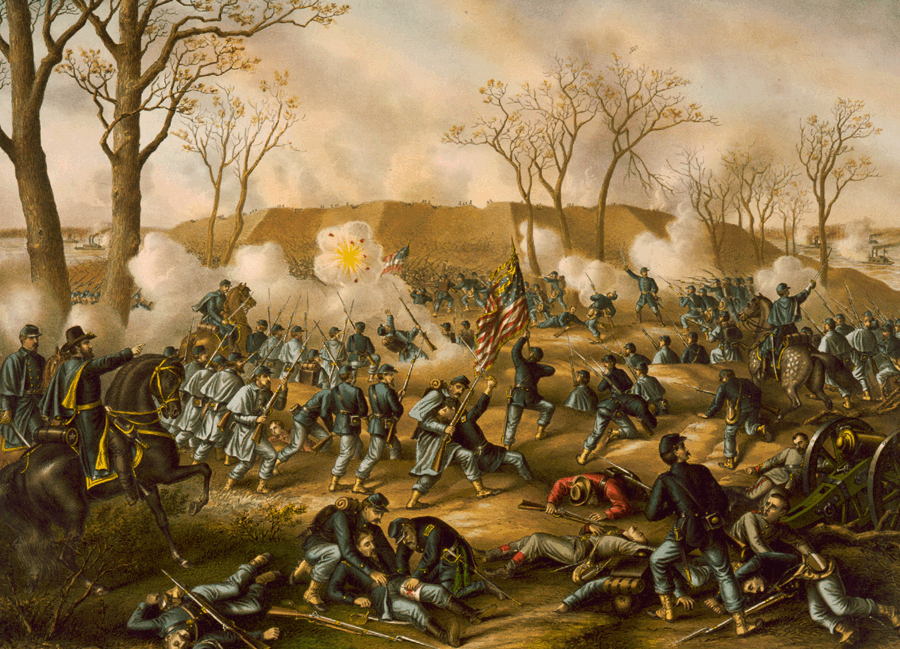
The Battle of Fort Donelson
Sited on the banks of the Cumberland River and only a matter of miles from Fort Henry, Fort Donelson was slated for Union assault even before General Ulysses S. Grant’s taking of Fort Henry. The close proximity between the two forts ensured that the Confederates would not be taken by surprise when Grant went onto Fort Donelson, but both sides knew that the ceding of Donelson would be a swift second defeat in a matter of days and inspire the Union to make further advances into Tennessee and Kentucky.
-
Grant’s Taking of Fort Henry
In early 1862, heartened by his troops’ performance at the Battle of Belmont, Brigadier General Ulysses S. Grant had determined that he was capable of making inroads into the Confederacy. Securing the network of rivers feeding into the Mississippi River as well as the Mississippi itself would hinder the Confederacy’s mobility and economy, and accomplishing this objective would bring him into two states that did not officially join the Confederacy but parts of which were Confederate-controlled: Kentucky and Tennessee. Bordering those states, on the banks of the Tennessee River, Grant saw a Confederate fort ripe for the plucking: Fort Henry. (more…)
